A 4-bay RAID enclosure is a versatile storage solution designed to house multiple hard disk drives (HDDs) within a single unit. These enclosures are commonly used in various applications where data storage, redundancy, and performance are essential. In this article, we will delve into the functionality of a 4-bay RAID enclosure, exploring how it works, its components, and the benefits it offers to users.
1. Components of a 4-Bay RAID Enclosure:
Drive Bays: A 4-bay RAID enclosure features four drive bays, each capable of accommodating a standard 3.5-inch HDD. These drive bays are designed with trays or slots for easy insertion and removal of the hard drives. The drive bays are typically located on the front or back panel of the enclosure, allowing users to access and swap out drives as needed.
RAID Controller: The RAID controller is a key component of a 4-bay RAID enclosure, responsible for managing the configuration and operation of the connected hard drives. The RAID controller supports various RAID levels, such as RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, and RAID 10, each offering different levels of data protection, performance, and storage efficiency.
Connectivity Ports: A 4-bay RAID enclosure is equipped with connectivity ports for connecting to external devices such as computers, servers, or network switches. Common connectivity options include USB, eSATA, Thunderbolt, and Ethernet (for network-attached storage or NAS enclosures). These ports facilitate data transfer and communication between the enclosure and external devices.
Power Supply: The power supply unit (PSU) provides electrical power to the 4-bay RAID enclosure, supplying energy to the hard drives, RAID controller, and other internal components. The PSU is typically integrated into the enclosure and may feature multiple power connectors to support the connected hard drives.



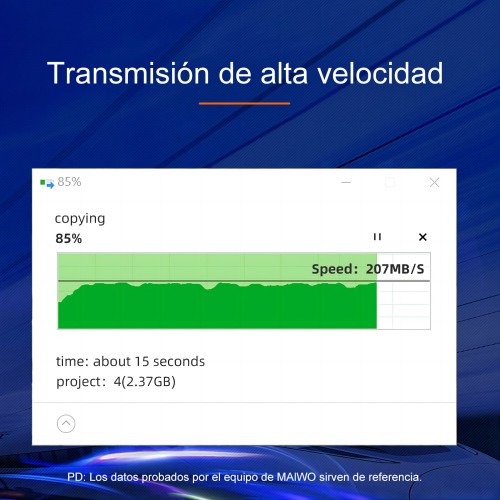
2. How a 4-Bay RAID Enclosure Works:
Drive Installation: The first step in using a 4-bay RAID enclosure is to install the hard drives into the drive bays. Users can simply slide the HDDs into the designated trays or slots and secure them in place using screws or locking mechanisms. The drive bays are numbered for easy identification and organization.
RAID Configuration: Once the hard drives are installed, users can configure the RAID settings using the RAID controller. This involves selecting the desired RAID level and defining parameters such as data striping, mirroring, parity, and hot spare configuration. The RAID controller manages the distribution of data across the hard drives according to the selected RAID configuration.
Data Access and Management: With the RAID configuration set up, users can start storing and accessing data on the 4-bay RAID enclosure. The RAID controller ensures that data is distributed evenly across the hard drives, optimizing performance and maximizing storage capacity. Users can access the data through connected devices such as computers, servers, or network-attached storage (NAS) systems.
Redundancy and Fault Tolerance: One of the key advantages of using a 4-bay RAID enclosure is its support for data redundancy and fault tolerance. Depending on the RAID configuration chosen, the enclosure can withstand the failure of one or more hard drives without losing data. In RAID 1 (mirroring), for example, data is duplicated across multiple drives, ensuring that if one drive fails, the data remains accessible on the mirrored drive.
Expansion and Scalability: As storage needs grow, users can easily expand the storage capacity of a 4-bay RAID enclosure by adding additional hard drives to the empty drive bays. The RAID controller supports dynamic expansion, allowing users to seamlessly integrate new drives into the existing RAID configuration without disrupting data access or performance.
3. Benefits of a 4-Bay RAID Enclosure:
Enhanced Data Protection: RAID configurations provide redundancy and fault tolerance, ensuring that data remains accessible even in the event of drive failure.
Improved Performance: By distributing data across multiple drives and leveraging parallel data access, RAID configurations enhance storage performance and speed.
Increased Storage Capacity: With support for multiple hard drives, a 4-bay RAID enclosure offers significantly increased storage capacity compared to individual drives.
Centralized Data Management: A 4-bay RAID enclosure allows users to centralize their data storage and management, simplifying access and organization of files across multiple devices.
In conclusion, a 4-bay RAID enclosure is a versatile and efficient storage solution that offers enhanced data protection, improved performance, increased storage capacity, and centralized data management. By leveraging RAID configurations and multiple hard drives, users can optimize storage efficiency, ensure data integrity, and streamline data access in various applications. Whether used for personal file storage, business-critical data management, or multimedia content creation, a 4-bay RAID enclosure provides reliability, flexibility, and scalability to meet diverse storage needs.